Custom Events and Conversions in GA4

Implementing Custom Conversions in GA4
Understanding Custom Conversions in GA4
Custom conversions in Google Analytics 4 (GA4) are crucial for tracking actions that aren't predefined by standard events. This allows businesses to gain a deeper understanding of user behavior beyond simple page views and clicks. By defining custom events, you can meticulously monitor specific user interactions, such as completing a form, downloading a file, or engaging with a specific product feature. This level of granular detail is essential for optimizing marketing strategies and refining user experiences.
Understanding the nuances of custom conversions is paramount. It involves meticulously defining the event parameters, ensuring accurate data collection, and utilizing these insights to enhance marketing campaigns and user journeys. Effective implementation leads to a more comprehensive view of user engagement and allows for more targeted and effective marketing strategies.
Defining Custom Events
Defining custom events is the foundation of implementing custom conversions. This involves identifying specific actions users take on your website or app that are valuable to your business. For example, signing up for a newsletter, adding an item to a shopping cart, or completing a purchase. Each event needs a unique name that clearly describes the action. Beyond the name, parameters are essential to provide context. These parameters allow you to categorize and further analyze the different types of interactions.
Setting Up Custom Conversion Parameters
Parameters provide crucial context for your custom events. They're essentially labels that add detail and structure to the data. Consider the parameters required to capture the full scope of user engagement for a specific event. For example, for a product added to cart event, parameters could include the product name, category, price, and quantity. This richer data allows for more sophisticated analysis and reporting.
Careful consideration of parameter selection is essential for accurate and meaningful data. The more relevant parameters you define, the more in-depth your analysis will be, enabling better decision-making and optimization strategies.
Implementing Custom Conversions with Tags
Implementing custom conversions often involves using tracking tags or libraries to capture the events. These tags or libraries need to be correctly integrated into your website or app code. This integration is critical to ensure that the events are accurately recorded and sent to GA4. The process usually involves triggering the custom event whenever the desired action occurs on your platform.
Proper implementation of these tags is key. Without correct implementation, the data collected won't be accurate, leading to flawed insights and ineffective strategies.
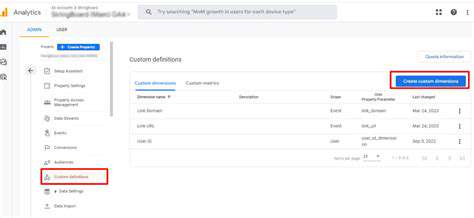
Using the GA4 Conversion Tracking Interface
Once the custom events are implemented, you'll need to configure them within the GA4 interface. This involves setting up conversion parameters, assigning values to conversions, and defining conversion goals. This allows you to track the success of specific marketing campaigns and user interactions. Understanding how to navigate the GA4 conversion tracking interface is essential for effective implementation and measurement.
This interface is crucial for defining how conversions are tracked, monitored, and ultimately used to improve your business's performance.
Optimizing Custom Conversions for Accuracy
Optimizing custom conversions for accuracy is an ongoing process. Regular review and testing are essential to ensure the events are being tracked correctly. This involves checking the parameters, verifying the tag implementation, and confirming that the data is being sent to GA4 accurately. This iterative approach ensures that the data you're using to make decisions is as precise and reliable as possible.
Ensuring accuracy is paramount to gaining actionable insights. Inaccurate data can lead to flawed decisions and ultimately impact your marketing and business strategies.
Troubleshooting Conversion Tracking Issues
Troubleshooting conversion tracking issues can be challenging but is vital for reliable data. Common problems include incorrect tag implementation, missing parameters, or misconfigurations within the GA4 interface. Thorough debugging is necessary to pinpoint the source of the issue. Documentation and thorough reviews of your tracking implementation are essential in resolving these issues. Testing and validation are critical steps in the process.
Read more about Custom Events and Conversions in GA4
Hot Recommendations
- Personalizing Email Content with User Behavior
- Geofencing for Event Attendance Tracking
- Reputation Management on Social Media
- UGC Beyond Photos: Videos, Testimonials, and More
- The Future of Data Privacy Regulations
- Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP) Benefits and Implementation
- The Future of CRM: AI and Voice Integration
- Google Ads Smart Bidding Strategies: Maximize Value
- Common A/B Testing Pitfalls to Avoid
- Local SEO Strategies for Small Businesses