Programmatic for App Install Campaigns
Introduction to Programmatic App Install Campaigns
Understanding the Core Concepts
Programmatic app development involves using code to build and control applications. This contrasts with traditional app development, which often relies on visual interfaces and drag-and-drop tools. Understanding the underlying logic and structure of an application through code allows for greater customization and efficiency. Programmatic app development is essential for tasks that require complex interactions, automation, and data manipulation. It's a powerful technique for creating dynamic and responsive applications that adapt to user needs and data changes.
A fundamental aspect of programmatic app development is the use of programming languages like Python, Java, or JavaScript. These languages provide the tools and syntax necessary to create the instructions that guide the application's behavior. Developers use these languages to define functions, create variables, and manage data flow within the app. Mastering these languages is crucial for building and maintaining any significant programmatic application.
Key Programming Languages and Tools
Several programming languages are commonly used in programmatic app development. Python, known for its readability and versatility, is a popular choice for its broad range of libraries and frameworks. Java, a robust and widely used language, is often favored for its platform independence and efficiency. JavaScript, primarily used for front-end development, is also applicable in back-end processes, connecting to databases and APIs. Choosing the right language often depends on the specific needs of the application and the developer's expertise.
Alongside the languages, various tools and frameworks are vital for streamlining the development process. Frameworks like React or Angular provide pre-built components and structures, accelerating development. Libraries like TensorFlow or PyTorch offer advanced functionalities for machine learning integration. These tools can significantly enhance developer productivity and allow for more efficient code management.
Building the Application Architecture
A well-structured application architecture is critical for the long-term maintainability and scalability of a programmatic app. Developers need to carefully consider the different components and their interactions. Modularity, where the application is divided into smaller, independent modules, contributes to code organization and reduces complexity. Employing appropriate design patterns helps ensure code reusability and maintainability, leading to easier updates and bug fixes. This structure is essential to ensure the app functions reliably and can be updated and improved over time.
Data Management and Handling
Data management plays a crucial role in programmatic app development. Applications often need to interact with data from various sources, whether it be databases, APIs, or user inputs. Developers must implement robust mechanisms for data validation and security. Efficient data handling is essential to ensure smooth data flow and application performance. Security is paramount when dealing with sensitive data. Implementing secure data protocols and encryption techniques is critical to protect user information and prevent unauthorized access.
Testing and Debugging
Thorough testing and debugging are indispensable parts of the programmatic app development lifecycle. Developers need to create robust test suites to ensure that the application functions correctly under various conditions. Debugging tools and techniques are essential for identifying and resolving errors in the code. Implementing automated testing allows for quicker feedback on code changes and helps prevent bugs from reaching production. Debugging effectively and efficiently is vital for producing reliable and stable applications.
Targeting Strategies for App Install Campaigns
Understanding Your Target Audience
Before diving into specific targeting strategies, a deep understanding of your ideal app user is crucial. This involves identifying key demographics, psychographics, and behavioral patterns. Analyzing user data from your existing user base, as well as market research, can help you define characteristics such as age, location, interests, and app usage habits. Understanding these factors helps to ensure your advertising resonates with the right people and improves your campaign ROI.
Location-Based Targeting
Location-based targeting allows you to show your ads to users in specific geographic areas. This is particularly valuable for app installs targeting users in certain regions. You can target users based on their current location, historical locations, or even proximity to specific points of interest. Precise location targeting can significantly increase the relevance of your ads and improve the likelihood of conversions.
For example, if your app is designed for local services, you can target users within a specific radius of your business locations. This approach ensures your ads are seen by potential customers who are most likely to use your app.
Demographic Targeting
Demographic targeting involves segmenting your audience based on characteristics like age, gender, income, and education level. This approach can be highly effective for app installs, allowing you to tailor your messaging to specific user groups. For example, if your app is aimed at a younger demographic, you might use different imagery and language than if it's targeting a more mature audience.
Interest-Based Targeting
Interest-based targeting focuses on reaching users who have demonstrated an interest in specific topics or categories. Using this method, you can show your ads to users actively engaged with relevant content, apps, or websites. For example, if your app is a fitness app, you can target users who have shown interest in fitness-related topics on social media or other platforms. This approach ensures that your ad message aligns with the user's existing interests, increasing engagement and conversion rates.
Behavioral Targeting
Behavioral targeting goes beyond interests and focuses on user actions and patterns. This involves analyzing user behavior on various platforms, like app usage, website visits, and online searches. By understanding how users interact with different platforms and apps, you can tailor your messaging to their specific needs and preferences. This approach is particularly helpful for targeting users who have demonstrated a history of using apps similar to yours. It allows for a more refined and effective approach to app install campaigns.
Retargeting Strategies
Retargeting is a powerful strategy to reach users who have previously interacted with your app or website. This can include users who have visited your app's landing page, but haven't yet installed it. By showing targeted ads to these users, you can re-engage them and encourage installation. Retargeting campaigns can significantly increase conversion rates, as users who have already expressed interest are more likely to convert.
Measuring and Optimizing Performance for App Installs
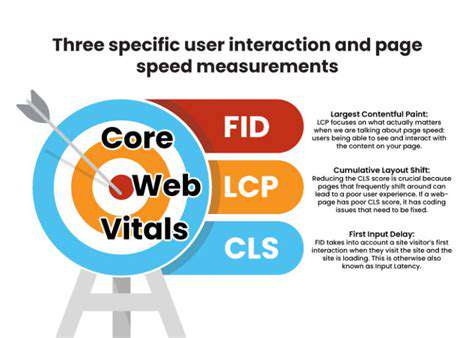
Defining Performance Metrics
A crucial first step in measuring and optimizing performance is establishing clear and quantifiable metrics. These metrics should align directly with business objectives, providing a concrete way to assess progress and identify areas for improvement. Defining these metrics early allows for a focused approach, avoiding the trap of measuring everything and optimizing nothing. Clearly defined metrics provide a benchmark against which future performance can be compared, enabling objective evaluation.
Different types of performance metrics are suitable for various functions. For example, in sales, metrics might focus on conversion rates, customer acquisition costs, and average order value. In marketing, metrics might encompass website traffic, engagement rates, and lead generation. Choosing relevant metrics is critical to understanding and improving the specific area of focus.
Identifying Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Once metrics are defined, identifying the most important Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) is essential. KPIs are the metrics that most significantly impact business objectives. Focusing on these KPIs enables a targeted approach to optimization, maximizing efficiency and resource allocation. Effective identification requires a thorough understanding of the business processes and their relationship to overall goals.
A good KPI should be measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). For example, a KPI for customer satisfaction might be the average customer rating on a feedback survey, collected over a specific timeframe.
Data Collection and Analysis
Reliable data collection is fundamental to accurate performance measurement. This involves implementing systems to capture the necessary data points, ensuring data integrity, and establishing a robust data storage and retrieval process. Reliable data is the foundation for effective analysis and subsequent optimization.
Analyzing collected data involves identifying trends, patterns, and correlations. Tools like spreadsheets, dashboards, and specialized software are often used to visualize and interpret the data, revealing insights into performance bottlenecks and areas of high potential.
Benchmarking Performance
Benchmarking against industry standards or competitors' performance provides valuable context for evaluating current performance levels. This helps in identifying areas where the organization excels and areas where improvement is needed. Benchmarking allows for the identification of best practices and opportunities for innovation.
Performance Gaps and Improvements
Identifying performance gaps between desired and actual performance levels is crucial for driving improvement. This analysis should pinpoint areas needing attention and prioritize improvement efforts based on impact and feasibility. Recognizing and addressing these gaps is critical for achieving optimal performance.
Implementation of Optimizations
Once performance gaps are identified, implementing targeted optimization strategies is necessary. This might involve process improvements, technology upgrades, or changes in staffing or resource allocation. Careful planning and execution are vital to ensure that optimization efforts yield the desired results. Successful implementation requires clear communication and collaboration among all stakeholders.
Monitoring and Evaluation
Continuous monitoring and evaluation of performance after implementing optimizations are essential to assess the effectiveness of changes. Regular data collection and analysis help determine if the optimizations are yielding the intended results and to identify any unforeseen consequences. Regular monitoring provides a feedback loop, enabling adjustments to strategies as needed. This iterative approach ensures that the optimization process remains dynamic and responsive to changing conditions.
Read more about Programmatic for App Install Campaigns
Hot Recommendations
- Personalizing Email Content with User Behavior
- Geofencing for Event Attendance Tracking
- Reputation Management on Social Media
- UGC Beyond Photos: Videos, Testimonials, and More
- The Future of Data Privacy Regulations
- Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP) Benefits and Implementation
- The Future of CRM: AI and Voice Integration
- Google Ads Smart Bidding Strategies: Maximize Value
- Common A/B Testing Pitfalls to Avoid
- Local SEO Strategies for Small Businesses