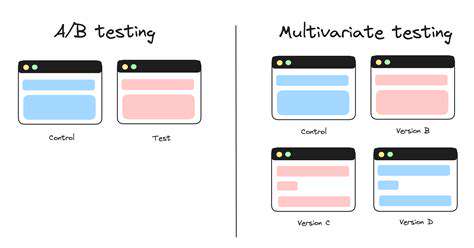
Multivariate Testing for Complex UX Changes
Defining Complex UX Changes in the Context of MVT
Defining the Scope of Change
Understanding the full scope of a complex UX change is crucial for successful implementation. This process goes beyond superficial problem identification; it demands an exhaustive examination of the current user journey, including every interaction point and potential friction area. Rigorous investigation and evaluation are indispensable for pinpointing the underlying causes of user dissatisfaction and recognizing deficiencies in the existing design framework. Techniques such as in-depth user interviews, comprehensive usability assessments, and meticulous data scrutiny are employed to develop a holistic view of user demographics and requirements.
A precisely delineated scope clearly specifies which features, functions, and user pathways will undergo modification. Establishing firm project parameters is critical to prevent uncontrolled expansion of project deliverables and maintain adherence to both budgetary constraints and timelines.
Identifying Key Stakeholders
Successful UX transformations require the early identification of all critical stakeholders across the organization. This encompasses not only design professionals but also representatives from product strategy, development teams, promotional departments, and customer service units. Incorporating diverse departmental perspectives through structured collaboration ensures unified commitment to project objectives throughout all phases of development.
Analyzing User Needs and Behaviors
The foundation of impactful UX modifications lies in meticulous analysis of user requirements and interaction patterns. This investigation should extend beyond basic questionnaires to incorporate ethnographic research methods, behavioral observation studies, and sophisticated analysis of usage analytics. The research must reveal not just user requirements but the fundamental motivations behind these needs and current system interaction patterns.
This empirical methodology guides design decisions, ensuring proposed modifications directly target identified user pain points. Comprehensive understanding of user psychology and behavioral patterns facilitates the creation of genuinely user-focused experience solutions.
Defining Measurable Success Metrics
The establishment of unambiguous, quantifiable success criteria is fundamental for assessing UX modification effectiveness. These indicators should satisfy SMART criteria - being specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-constrained. Potential metrics include conversion ratios, task completion durations, user satisfaction indices, and overall platform engagement levels. Well-defined metrics enable impartial evaluation of the modification's operational impact.
Implementing these measurement protocols from inception allows teams to monitor progress, detect improvement areas, and ultimately substantiate the business value of UX enhancements to decision-makers. Continuous performance tracking facilitates timely adjustments to ensure project alignment with strategic objectives.
Developing a Detailed Implementation Plan
Complex UX initiatives demand meticulously structured execution blueprints. These plans should specify task assignments, temporal milestones, resource distribution, and communication protocols required for successful deployment. Comprehensive planning guarantees adherence to project schedules and financial constraints. Detailed preparation enables optimal resource utilization, effective dependency management, and anticipation of potential obstacles.
Contingency strategies for unexpected developments should be incorporated, ensuring project resilience against technical complications, unanticipated user responses, and scheduling deviations.
Managing User Adoption and Feedback
Effective change management and continuous feedback integration are paramount for sustainable UX improvement. This necessitates comprehensive educational campaigns to familiarize users with modifications and provide clear operational guidance for new features. Proactive engagement strategies promote seamless transitions and mitigate resistance to change.
Implementation of robust feedback collection mechanisms throughout the adoption phase enables iterative refinement and maintains user-centric design principles. This continuous evaluation cycle is critical for optimizing user experience in response to evolving needs and preferences.
Developing Effective Multivariate Test Hypotheses
Formulating Clear Hypotheses
The initial phase of constructing impactful multivariate test hypotheses involves precise definition of targeted improvement areas within digital properties. This requires establishing quantifiable objectives such as enhanced conversion performance, increased transactional values, or reduced early exit rates. Rather than ambiguous statements about general experience enhancement, hypotheses should focus on specific interface elements with measurable impact potential.
Extensive investigation of user activity patterns, competitive benchmarking, and industry analysis forms the foundation for hypothesis generation. Deep comprehension of user requirements, pain points, and behavioral drivers significantly enhances hypothesis quality and testing effectiveness.
Defining Key Variables and Metrics
Successful multivariate testing requires unambiguous identification of test parameters and evaluation criteria. Variable selection may include chromatic treatments, structural modifications, or content variations. Strategic alignment of measurement criteria with business objectives is paramount - whether evaluating registration completions, average order values, or other key performance indicators.
Precise definition of impact measurement methodologies is equally critical, potentially involving tracking of interaction rates, conversion percentages, session durations, or abandonment metrics. Metric selection directly influences result interpretation and hypothesis validation.
Considering Potential Interactions
Multivariate analysis frequently encounters complex variable interdependencies. Effective hypothesis formulation requires anticipation and accommodation of these potential interactions. For instance, chromatic modifications may produce divergent effects when combined with various background treatments or textual content.
Comprehensive test design must account for these potential synergies through sophisticated experimental structures that isolate individual variable impacts while evaluating combined effects.
Establishing a Baseline and Defining Success
Preliminary performance benchmarking constitutes an essential prerequisite for meaningful multivariate testing. Comprehensive measurement of current interface metrics provides the reference framework for evaluating modification impacts. This empirical foundation enables accurate quantification of change effects and data-informed decision making.
Explicit success criteria definition - incorporating specific performance improvement targets - ensures hypothesis testability and eliminates interpretive ambiguity. Implementation of SMART objectives maintains analytical focus and facilitates progress tracking throughout the testing lifecycle.
Read more about Multivariate Testing for Complex UX Changes
Hot Recommendations
- Personalizing Email Content with User Behavior
- Geofencing for Event Attendance Tracking
- Reputation Management on Social Media
- UGC Beyond Photos: Videos, Testimonials, and More
- The Future of Data Privacy Regulations
- Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP) Benefits and Implementation
- The Future of CRM: AI and Voice Integration
- Google Ads Smart Bidding Strategies: Maximize Value
- Common A/B Testing Pitfalls to Avoid
- Local SEO Strategies for Small Businesses