Consumer Consent Management: Best Practices
Defining a Robust Consumer Consent Management Framework
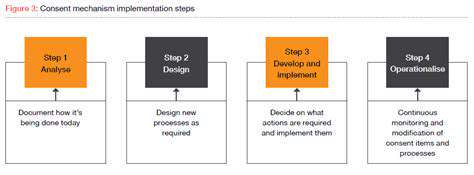
Understanding the Fundamentals of Consumer Consent
In today's digital landscape, consumer consent has become a cornerstone of ethical business operations. At its core, consumer consent represents the explicit permission individuals grant to organizations regarding the collection, processing, and sharing of their personal information. What makes this agreement valid isn't just its existence, but its clarity, simplicity, and accessibility to the average person. When companies fail to secure proper consent, they risk legal consequences and significant damage to their brand reputation. More importantly, they erode the fundamental trust that forms the basis of customer relationships.
Modern consent frameworks must move beyond superficial compliance. They should actively involve consumers in the process, clearly explaining what specific data elements are being gathered, the precise purposes for their use, and all potential third-party recipients. True consumer empowerment means giving people straightforward mechanisms to modify or revoke their consent at any point, without facing unnecessary barriers. This level of transparency and control demonstrates an organization's genuine commitment to ethical data stewardship and builds lasting customer confidence.
Implementing Effective Consent Mechanisms
Creating meaningful consent processes requires a thoughtful, multi-dimensional strategy. Organizations should develop privacy policies that strike a balance between comprehensiveness and readability, ensuring they're accessible to people with varying levels of technical understanding. These documents must articulate in plain language exactly what data will be collected, for what specific business purposes, and who might have access to it. Only with this level of detail can consumers make truly informed decisions about their personal information.
In practice, companies should deploy intuitive consent interfaces - whether through interactive digital forms, preference centers, or dedicated management portals. These tools must offer genuine flexibility, allowing individuals to selectively opt in or out of different data uses. The combination of straightforward language, logical information architecture, and accessible support options creates an environment where consumers can comfortably exercise their privacy choices. When executed well, these mechanisms not only ensure compliance but also transform data collection from a compliance exercise into a trust-building opportunity.
Maintaining Compliance and Evolving Standards
Keeping pace with the dynamic regulatory environment presents an ongoing challenge for organizations managing consumer consent. Regulations like GDPR, CCPA, and emerging frameworks continue to evolve, requiring businesses to regularly assess and update their compliance strategies. This isn't merely about avoiding penalties - it's about maintaining alignment with shifting legal expectations and societal norms regarding data privacy.
Perhaps more significantly, consumer expectations around data privacy continue to mature. Today's individuals are increasingly sophisticated about their digital rights and expect organizations to demonstrate genuine respect for their personal information. Companies that consistently show transparency and proactive data stewardship don't just comply with regulations - they differentiate themselves in the marketplace and forge stronger customer relationships. This demands continuous evaluation and refinement of consent approaches to reflect both regulatory changes and evolving consumer preferences.
Staying Compliant with Evolving Data Privacy Regulations
Understanding the Landscape of Data Privacy Regulations
Today's global business environment presents a complex web of data protection requirements that vary significantly by jurisdiction. From the comprehensive approach of Europe's GDPR to California's consumer-focused CCPA and its subsequent iterations, organizations must maintain current knowledge of these frameworks' specific provisions and enforcement trends. The stakes are particularly high for businesses operating across borders, as non-compliance can result in substantial financial penalties and reputational harm.
The challenge intensifies for multinational organizations that must navigate sometimes conflicting requirements between different regulatory regimes. Developing a nuanced understanding of how these regulations interact - and where they diverge - is essential for creating compliance strategies that work across all operational territories.
Implementing Robust Consent Management Practices
Effective consent management in this regulatory environment demands more than just checking legal boxes. It requires designing systems that make transparency and user control fundamental components of the data collection process. This means presenting consent requests in clear, unambiguous language, organized in ways that help consumers understand the implications of their choices. Granular options should allow individuals to selectively permit different types of data processing rather than being forced into all-or-nothing decisions.
When implemented thoughtfully, these practices do more than ensure compliance - they create positive user experiences that reinforce trust. They also provide operational benefits by establishing clear parameters for data usage, reducing compliance risks, and creating more accurate customer preference profiles.
Developing a Comprehensive Data Inventory
A thorough data inventory serves as the foundation for effective privacy management. This living document should catalog all personal data streams within the organization, including detailed information about data categories, collection methods, processing purposes, storage locations, and retention periods. Maintaining this inventory requires regular updates to reflect new data practices and sunset obsolete ones, ensuring the organization always has an accurate picture of its data ecosystem.
Establishing Secure Data Storage and Transmission Protocols
Data security forms the critical backbone of any privacy program. Organizations must implement and maintain robust technical and organizational measures to protect personal information throughout its lifecycle. This includes employing strong encryption standards for data at rest and in transit, implementing rigorous access controls, and conducting regular security assessments to identify and address vulnerabilities.
For data in motion, secure transmission protocols are non-negotiable. Organizations should establish encrypted communication channels for all data transfers and implement additional safeguards like tokenization or pseudonymization where appropriate. These measures not only protect against external threats but also help prevent internal misuse of sensitive information.
Developing a Data Breach Response Plan
Despite best efforts, data breaches remain an ever-present risk in today's digital environment. A well-constructed response plan is essential for mitigating their impact. This plan should establish clear protocols for incident detection, containment, assessment, and notification, with defined roles and responsibilities across the organization. It should also include templates for regulatory and consumer communications to ensure timely, compliant responses.
Regular testing through tabletop exercises helps identify gaps in the response plan before an actual incident occurs. These simulations also familiarize team members with their roles, ensuring a more coordinated response when needed. Beyond technical remediation, the plan should address reputational management strategies to maintain consumer trust following an incident.
Training and Educating Employees on Data Privacy
Employees serve as both the first line of defense and potential vulnerabilities in data protection. Comprehensive, role-specific training programs ensure all staff understand their responsibilities regarding personal data handling. Training should cover legal requirements, organizational policies, and practical guidance for common scenarios employees might encounter. Regular refreshers and updates help maintain awareness as regulations and threats evolve.
Regularly Reviewing and Updating Compliance Strategies
Privacy compliance isn't a one-time project but an ongoing process requiring constant attention. Organizations should establish regular review cycles to assess their compliance posture against changing regulations and business practices. This includes monitoring legislative developments, regulatory guidance, and enforcement trends in all relevant jurisdictions.
Internal audits and third-party assessments provide valuable objectivity in evaluating program effectiveness. These reviews should identify control gaps, assess risk levels, and recommend improvements. By institutionalizing this continuous improvement mindset, organizations can maintain compliance more effectively and adapt quickly to new requirements.
Measuring and Monitoring the Effectiveness of Your Program
Measuring Performance Metrics
Effective program evaluation begins with selecting meaningful metrics that directly align with strategic objectives. These Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) should provide actionable insights into program effectiveness across multiple dimensions. For instance, in assessing privacy program performance, relevant metrics might include consent rates, preference modification frequencies, complaint volumes, or audit findings. The selection process should focus on metrics that truly reflect program health and business impact rather than vanity metrics that look impressive but offer little substantive value.
Longitudinal tracking of these indicators reveals trends that single data points cannot, allowing organizations to distinguish between temporary fluctuations and meaningful patterns. This temporal analysis helps identify what's working well and where adjustments may be needed. Sophisticated programs will also examine correlations between different metrics - for example, whether improvements in consent transparency correlate with increased customer satisfaction scores or reduced complaint volumes. These relationships often reveal insights that individual metrics cannot.
Monitoring Implementation Progress
Successful program execution requires diligent progress tracking against established timelines and milestones. This involves creating a detailed implementation roadmap with clear deliverables and accountability assignments. Regular checkpoint reviews help ensure activities stay on schedule while allowing for course correction when needed. Modern project management tools can automate much of this tracking while providing real-time visibility to all stakeholders.
Transparent reporting mechanisms create organizational accountability by making progress (or lack thereof) visible to all relevant parties. These reports should highlight accomplishments, identify roadblocks, and propose solutions in a format that facilitates quick decision-making. Effective reporting balances quantitative progress metrics with qualitative insights about implementation challenges and lessons learned.
Structured review meetings provide forums for deeper discussion of implementation issues. These sessions should encourage open dialogue about obstacles while maintaining focus on solutions. They're particularly valuable for identifying cross-functional dependencies or resource constraints that might not be apparent in individual team reports. The most effective reviews result in concrete action items with clear ownership and deadlines.
Resource monitoring represents another critical implementation oversight function. This involves tracking not just budget expenditures but also human capital allocation and utilization rates. Effective resource management ensures that teams have what they need when they need it, while also identifying opportunities to improve efficiency. Dashboards that visualize resource allocation against project timelines can help managers spot potential bottlenecks before they cause delays.
Read more about Consumer Consent Management: Best Practices
Hot Recommendations
- Personalizing Email Content with User Behavior
- Geofencing for Event Attendance Tracking
- Reputation Management on Social Media
- UGC Beyond Photos: Videos, Testimonials, and More
- The Future of Data Privacy Regulations
- Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP) Benefits and Implementation
- The Future of CRM: AI and Voice Integration
- Google Ads Smart Bidding Strategies: Maximize Value
- Common A/B Testing Pitfalls to Avoid
- Local SEO Strategies for Small Businesses